Infectious diseases that pass from a person to another during sexual contact are called sexually transmitted diseases ( STDs)
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) can exists in blood. this virus can hide in body cells, sometimes for years. In fact, you can become infected with HIV by having sex with an HIV infected person or through an injection by an infected needle. However, a freshly unwrapped sterile needle cannot transmit the infection. Also,the risk of getting HIV through blood transfusion is small because all donated blood is tested for the presence of HIV.
HIV cannot multiply outside the body, and it does not survive for long time in the environment. It's important to recognize that this virus cannot be transmitted by touching an infected person, by handling objects used by the person unless they are contaminated with body fluids, or from contact with a toilet seat.
An HIV infection can lead to Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS), which is a disease that attacks the body's immune system. HIV attacks T helper cells in the immune system. the virus enters T cells and multiply, so as when the bursts cells open, it releases more HIV. with time, so many T cells are destroyed and not enough B cells are stimulated to produce antibodies. As a result, the body has no longer an effective way to fight invading antigens nor to fight HIV. For this reason, people with HIV die from other diseases such as tuberculosis, cancer, etc..
A person can be infected with HIV and not show any symptoms of the infection for several years. Why does this characteristic make the spread of AIDS more likely ??
 source of image : Shanise Welch (shanisewelch.blogspot.com/)
source of image : Shanise Welch (shanisewelch.blogspot.com/)
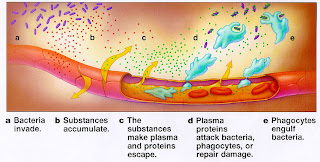
source of image: AIDS(www.nlm.nih.gov/.../ency/imagepages/17015.htm )


+(c)_7.jpg)



+(c)_1.jpg)
.jpg)